Learning a new language can be exciting—but also frustrating when you keep forgetting words you just learned. Have you ever encountered a word like “borrow”, looked up the meaning, felt like you understood it, and then forgotten it the next day? If so, you’re not alone—and it’s not your memory’s fault. The problem is how you’re learning.
Instead of memorizing vocabulary through direct translation, research and teaching experience show that using images can help retain vocabulary far more effectively. Images, mental associations, and visual techniques strengthen your brain’s connection to new words, helping you remember them faster and for longer.
In this article, we’ll explore three powerful methods that show how images help you retain vocabulary: using pictures, applying mnemonic tools, and building word maps. These techniques can make a big difference in how you learn and remember new English words.
1. Use Pictures to Trigger Memory
The simplest and most effective way to use visuals is to connect English words with pictures or images. According to English teacher and trainer Danielle Zelin, who has taught in countries like South Africa, Latvia, and Mauritius, humans naturally think in images—not in sentences.
“When we hear a sentence like ‘Yesterday, I went to the beach,’ we don’t see the sentence in our brain—we see the picture of the beach,” says Zelin.
This insight is crucial for language learners. When you see a word like “apple,” attaching it to a picture of an apple—rather than its translation—creates a direct connection to the concept. This connection strengthens memory.
Another expert, Cristiane Galvão, who has taught English in both the U.S. and Brazil for over 20 years, suggests creating your own visual dictionary. To do this, collect images from the internet and place them next to the corresponding English word. This works well for learners of all ages and skill levels.
Pro Tip for Your Visual Dictionary:
- If your goal is to reinforce known vocabulary, organize the images alphabetically and by topic.
- If you want to practice writing sentences, skip the organization and focus on sentence-building.
Visual dictionaries combine structure and creativity, turning your vocabulary study into an interactive experience.
2. Use Mnemonics to Strengthen Word Associations
Mnemonics are memory tools that help you recall information using associations, mental imagery, or stories. These tools work exceptionally well for language learning, especially when paired with similar-sounding keywords and creative pictures.
Take the word “bald”, which means “without hair.” It sounds like “ball.” So you can imagine a ball with a face but no hair—just like a bald head. Picture this image clearly for about 15 seconds. Later, when you need to remember “bald,” the picture will pop into your head and bring the meaning with it.
This is called the keyword mnemonic technique. World memory champion Alex Mullen calls it “the art of memory.” He explains that combining sound (keywords) with sight (mental images) is a highly effective way to store new words in long-term memory.
Try This:
- For the word “corral” (a pen or enclosure for animals), think of the similar word “coral.”
- Picture tiny stick figures trapped inside a sea coral—just like animals in a corral.
- The silly image helps lock the word’s meaning into your brain.
These memory shortcuts don’t just help you remember—they make learning fun and creative.
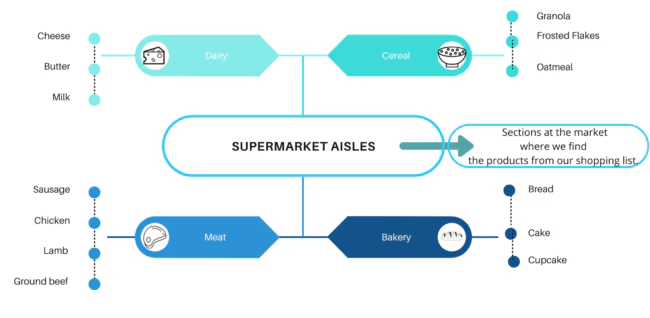
3. Build Word Maps for Stronger Connections
Another visual technique to retain vocabulary is creating word maps, also known as semantic maps or word webs. These maps help you organize words into meaningful relationships.
To make a word map:
- Start with a main word in the center of a page.
- Draw lines to related words, concepts, or categories.
For example, if your central word is “sharp”, your map might include “knife,” “scissors,” “paper,” and “blade.” This strategy helps you group vocabulary by meaning, which reinforces understanding and recall.
Both Zelin and Galvão emphasize the importance of context when using word maps. Galvão suggests discussing the topic and using images before building the map to give words deeper meaning. Without that context, the word map might feel like just another list of words to memorize.
“Vocabulary is a big part of language learning. So, the more meaningful it is, the easier it is for the student to absorb,” Galvão says.
Why Images Help Retain Vocabulary Better
Here’s a quick summary of why images help retain vocabulary so effectively:
- Visual cues activate the brain’s memory centers.
- Mental images create deeper neural connections.
- Mnemonics turn abstract words into memorable stories.
- Word maps provide structure and meaning.
- Pictures bypass the need for translation, linking English words directly to real-world concepts.
Instead of relying on rote memorization and translation, these image-based strategies allow learners to internalize vocabulary naturally and effectively. Whether you’re a beginner or advanced learner, adding visuals to your language study routine can lead to faster results and a better understanding of English.
Learning vocabulary doesn’t have to be difficult. With the right tools—like pictures, mnemonics, and word maps—you can build a strong memory system that works with your brain, not against it.
So the next time you forget what a word means, don’t blame your memory. Try making a mental image, drawing a word map, or adding a new word to your visual dictionary. You’ll be surprised at how much easier vocabulary retention becomes.